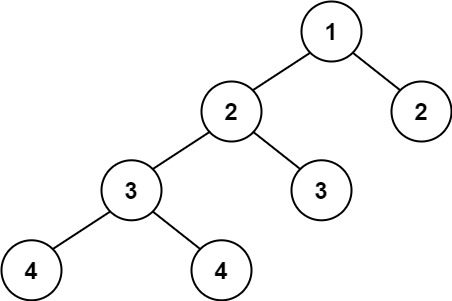
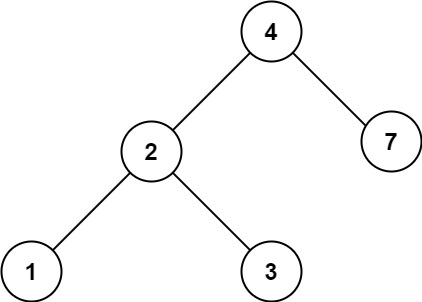
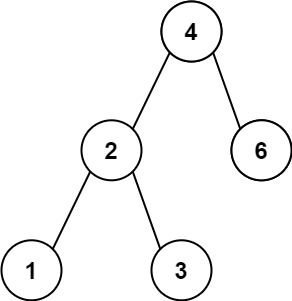
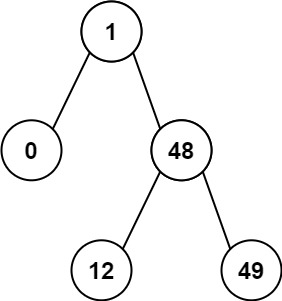
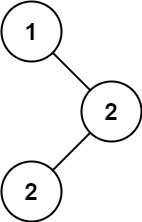
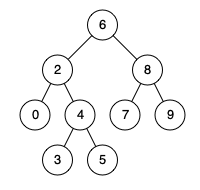
二叉树 1、二叉树的前序遍历 给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历。
示例 1:
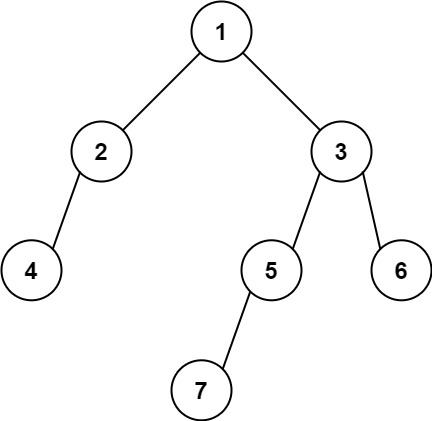
1 2 输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,2,3]
示例 2:
示例 3:
示例 4:
1 2 输入:root = [1,2] 输出:[1,2]
示例 5:
1 2 输入:root = [1,null,2] 输出:[1,2]
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <Integer>(); preOrder(root, result); return result; } public void preOrder (TreeNode root,List<Integer> result) { if (root == null ) { return ; } result.add(root.val); preOrder(root.left, result); preOrder(root.right, result); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) { return result; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); if (node.right != null ) { stack.push(node.right); } if (node.left != null ) { stack.push(node.left); } } return result; } }
2、二叉树的后序遍历 给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[3,2,1]
示例 2:
示例 3:
提示:
树中节点的数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
方案一:递归的方法
1.确定递归函数的返回值,参数
2.确定递归函数的终止条件
3.确定单层递归的逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); postorderTraver(root,result); return result; } public void postorderTraver (TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) { if (root == null ) return ; postorderTraver(root.left,result); postorderTraver(root.right,result); result.add(root.val); } }
迭代法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) { return result; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); if (node.left != null ) { stack.push(node.left); } if (node.right != null ) { stack.push(node.right); } } Collections.reverse(result); return result; } }
3、二叉树的中序遍历 给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
示例 3:
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); inorderTraver(root,result); return result; } public void inorderTraver (TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) { if (root == null ) return ; inorderTraver(root.left,result); result.add(root.val); inorderTraver(root.right,result); } }
迭代法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) { return result; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); TreeNode cur = root; while (!stack.isEmpty()) { if (cur.left != null ) { stack.push(cur.left); cur = cur.left; } else { TreeNode node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); if (node.right != null ) { stack.push(node.right); cur = node.right; } } } return result; } }
4、二叉树的统一迭代法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new LinkedList <Integer>(); Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); if (root == null ) return result; stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode tmp = stack.peek(); if (tmp != null ){ stack.pop(); if (tmp.right != null ){ stack.push(tmp.right); } if (tmp.left != null ){ stack.push(tmp.left); } stack.push(tmp); stack.push(null ); }else { stack.pop(); TreeNode target = stack.pop(); result.add(target.val); } } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new LinkedList <>(); Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); if (root == null ) return result; stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode temp = stack.peek(); if (temp != null ){ stack.pop(); if (temp.right != null ) { stack.push(temp.right); } stack.push(temp); stack.push(null ); if (temp.left !=null ) { stack.push(temp.left); } }else { stack.pop(); TreeNode target = stack.pop(); result.add(target.val); } } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new LinkedList <>(); Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); if (root == null ) return result; stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode temp = stack.peek(); if (temp != null ) { stack.push(null ); if (temp.right != null ) { stack.push(temp.right); } if (temp.left != null ) { stack.push(temp.left); } } else { stack.pop(); TreeNode target = stack.pop(); result.add(target.val); } } return result; } }
5、二叉树的层序遍历 https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例 1:
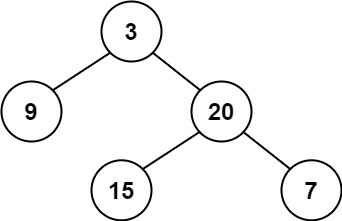
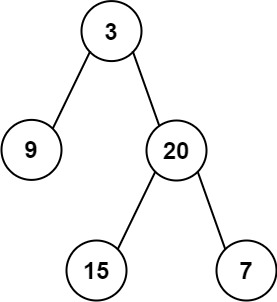
1 2 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
示例 2:
示例 3:
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [0, 2000] 内
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <List<Integer>>(); if (root == null ) return result; Queue<TreeNode> treeQue = new LinkedList <TreeNode>(); treeQue.offer(root); while (!treeQue.isEmpty()){ int size = treeQue.size(); List <Integer> itemList = new ArrayList <Integer>(); while (size > 0 ){ TreeNode item = treeQue.poll(); itemList.add(item.val); if (item.left != null ){ treeQue.offer(item.left); } if (item.right != null ){ treeQue.offer(item.right); } size--; } result.add(itemList); } return result; } }
一口气打10题:
102.二叉树的层序遍历(opens new window)
107.二叉树的层次遍历II(opens new window)
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值 自底向上的层序遍历 。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[15,7],[9,20],[3]]
示例 2:
示例 3:
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [0, 2000] 内
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom (TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> result = new LinkedList <List<Integer>>(); if (root == null ) { return result; } Queue <TreeNode> treeQue = new LinkedList <TreeNode>(); treeQue.offer(root); while (!treeQue.isEmpty()) { int size = treeQue.size(); List<Integer> itemList = new ArrayList <Integer>(); while (size > 0 ) { TreeNode tmp = treeQue.poll(); itemList.add(tmp.val); if (tmp.left != null ) { treeQue.offer(tmp.left); } if (tmp.right != null ) { treeQue.offer(tmp.right); } size--; } result.add(0 ,itemList); } return result; } }
在 Java 的 LinkedList 类中,add(int index, E element) 方法用于在指定位置 index 插入元素 element。当我们使用 result.add(0, itemList);,这意味着我们每次都在 result 列表的开头位置插入一个新的列表 itemList。
下面是这个操作背后的一些底层细节:
更新头尾指针:如果链表原来是空的,则新插入的节点既是头节点也是尾节点。如果链表不是空的,只需更新头节点指针(对于在开头插入的情况)
199.二叉树的右视图(opens new window)
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4] 输出: [1,3,4]
示例 2:
1 2 输入: [1,null,3] 输出: [1,3]
示例 3:
提示:
二叉树的节点个数的范围是 [0,100]
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 ``` - [637. 二叉树的层平均值(opens new window )](https: - [429. N叉树的层序遍历(opens new window )](https: - [515. 在每个树行中找最大值(opens new window )](https: - [116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针(opens new window )](https: - [117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II(opens new window )](https: - [104. 二叉树的最大深度(opens new window )](https: - [111. 二叉树的最小深度](https: #### 6 、翻转二叉树 给你一棵二叉树的根节点 `root` ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。 **示例 1 :** 
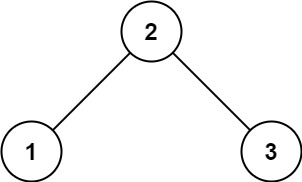
输入:root = [2,1,3]
输入:root = []
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 **提示:** - 树中节点数目范围在 `[0, 100]` 内 - `-100 <= Node.val <= 100` ```java //方案一,递归法(前序、后序都可以) class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return root; } swapTree(root); invertTree(root.left); invertTree(root.right); return root; } public void swapTree(TreeNode root) { TreeNode tmp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = tmp; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return root; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode temp = stack.peek(); if (temp != null ) { stack.pop(); if (temp.right != null ) { stack.push(temp.right); } stack.push(temp); stack.push(null ); if (temp.left != null ) { stack.push(temp.left); } } else { stack.pop(); TreeNode target = stack.pop(); swapTree(target); } } return root; } public void swapTree (TreeNode root) { TreeNode tmp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = tmp; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return root; } Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList <>(); deque.offer(root); while (!deque.isEmpty()) { for (int size = deque.size(); size > 0 ; size--) { TreeNode temp = deque.poll(); swapTree(temp); if (temp.left != null ) { deque.offer(temp.left); } if (temp.right != null ) { deque.offer(temp.right); } } } return root; } public void swapTree (TreeNode root) { TreeNode tmp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = tmp; } }
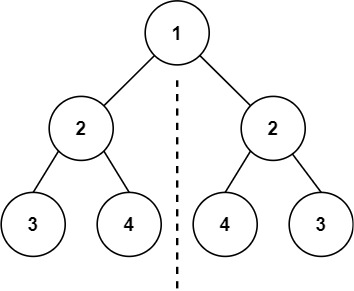
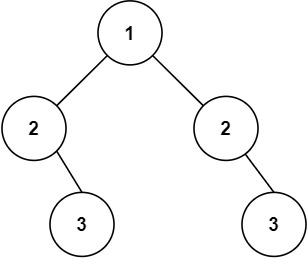
7、对称二叉树 给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 输出:true
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 输出:false
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [1, 1000] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶: 你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题吗?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return true ; } return compare(root.left,root.right); } public boolean compare (TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { if (left == null && right != null ) { return false ; } if (left != null && right == null ) { return false ; } if (left == null && right == null ) { return true ; } if (left.val != right.val) { return false ; } boolean outside = compare(left.left,right.right); boolean inside = compare(left.right,right.left); return outside && inside; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return true ; } Deque <TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList <>(); deque.offer(root.left); deque.offer(root.right); while (!deque.isEmpty()) { TreeNode right = deque.poll(); TreeNode left = deque.poll(); if (right == null && left != null ) { return false ; } if (right != null && left == null ) { return false ; } if (right == null && left == null ) { continue ; } if (right.val != left.val) { return false ; } deque.offer(left.left); deque.offer(right.right); deque.offer(left.right); deque.offer(right.left); } return true ; } }
两道相似的题:
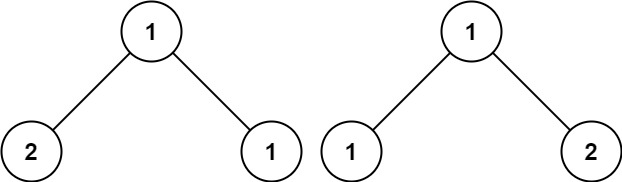
给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3] 输出:true
示例 2:
1 2 输入:p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2] 输出:false
示例 3:
1 2 输入:p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2] 输出:false
提示:
两棵树上的节点数目都在范围 [0, 100] 内
-10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public boolean isSameTree (TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (p == null && q != null ) { return false ; } if (p != null && q == null ) { return false ; } if (p == null && q == null ) { return true ; } if (p.val != q.val) { return false ; } boolean left = isSameTree(p.left,q.left); boolean right = isSameTree(p.right,q.right); return left && right; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public boolean isSameTree (TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (p == null && q == null ) { return true ; } Deque <TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList <>(); deque.offer(p); deque.offer(q); while (!deque.isEmpty()) { TreeNode rightTree = deque.poll(); TreeNode leftTree = deque.poll(); if (rightTree == null && leftTree !=null ) { return false ; } if (rightTree != null && leftTree == null ) { return false ; } if (rightTree == null && leftTree == null ) { continue ; } if (rightTree.val != leftTree.val) { return false ; } deque.offer(rightTree.left); deque.offer(leftTree.left); deque.offer(rightTree.right); deque.offer(leftTree.right); } return true ; }
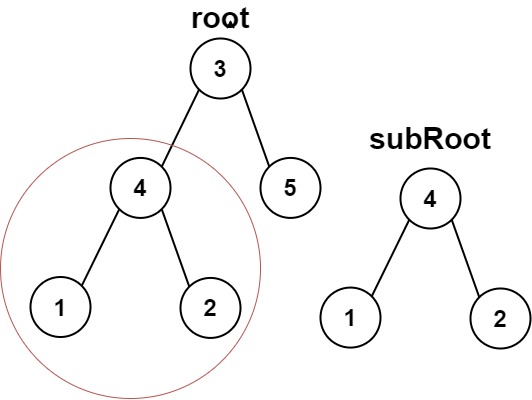
给你两棵二叉树 root 和 subRoot 。检验 root 中是否包含和 subRoot 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
二叉树 tree 的一棵子树包括 tree 的某个节点和这个节点的所有后代节点。tree 也可以看做它自身的一棵子树。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [3,4,5,1,2], subRoot = [4,1,2] 输出:true
示例 2:
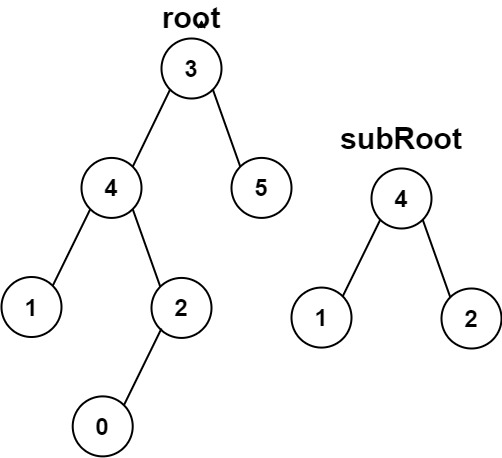
1 2 输入:root = [3,4,5,1,2,null,null,null,null,0], subRoot = [4,1,2] 输出:false
提示:
root 树上的节点数量范围是 [1, 2000]subRoot 树上的节点数量范围是 [1, 1000]-104 <= root.val <= 104-104 <= subRoot.val <= 104
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public boolean isSubtree (TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) { if (root == null ) { return false ; } if (isSametree(root,subRoot)) { return true ; } return isSubtree(root.left,subRoot) || isSubtree(root.right,subRoot); } public boolean isSametree (TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (p == null && q == null ) { return true ; } if (p == null || q == null ) { return false ; } if (p.val != q.val) { return false ; } boolean left = isSametree(p.left,q.left); boolean right = isSametree(p.right,q.right); return left && right; } }
8、二叉树的最大深度 给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:3
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [1,null,2] 输出:2
提示:
树中节点的数量在 [0, 104] 区间内。
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { int depth = 0; if (root == null) { return 0; } return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left)+1,maxDepth(root.right)+1); } }
给定一个 N 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
N 叉树输入按层序遍历序列化表示,每组子节点由空值分隔(请参见示例)。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] 输出:3
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] 输出:5
提示:
树的深度不会超过 1000 。
树的节点数目位于 [0, 104] 之间。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int maxDepth (Node root) { int depth = 0 ; if (root == null ) { return 0 ; } for (int i = 0 ;i<root.children.size();i++) { depth = Math.max(depth,maxDepth(root.children.get(i))); } return depth+1 ; } }
9、二叉树的最小深度 力扣题目链接
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:2
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6] 输出:5
提示:
树中节点数的范围在 [0, 105] 内
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int minDepth (TreeNode root) { int depth = 0 ; if (root == null ) { return depth; } Deque <TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList <>(); deque.offer(root); while (!deque.isEmpty()) { depth++; for (int i = deque.size(); i > 0 ; i--) { TreeNode tmp = deque.poll(); if (tmp.left != null ) { deque.offer(tmp.left); } if (tmp.right != null ) { deque.offer(tmp.right); } if (tmp.left == null && tmp.right == null ) { return depth; } } } return depth; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int minDepth (TreeNode root) { int depth = 0 ; if (root == null ) { return 0 ; } int left = minDepth(root.left); int right = minDepth(root.right); if (root.left == null ) { depth = right+1 ; } if (root.right == null ) { depth = left+1 ; } if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) { depth = 1 ; } if (root.left != null && root.right != null ) { depth = Math.min(left,right)+1 ; } return depth; } }
10、完全二叉树的节点个数 给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6] 输出:6
示例 2:
示例 3:
提示:
树中节点的数目范围是[0, 5 * 104]
0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 104题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
进阶: 遍历树来统计节点是一种时间复杂度为 O(n) 的简单解决方案。你可以设计一个更快的算法吗?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int countNodes (TreeNode root) { int node = 0 ; if (root == null ) { return 0 ; } int left = countNodes(root.left); int right = countNodes(root.right); node = left + right + 1 ; return node; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int countNodes (TreeNode root) { int result = 0 ; if (root == null ) { return 0 ; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <TreeNode>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); while (size > 0 ) { TreeNode tmp = queue.poll(); result++; size--; if (tmp.left != null ) { queue.offer(tmp.left); } if (tmp.right != null ) { queue.offer(tmp.right); } } } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int countNodes (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return 0 ; } int leftdepth = 0 ; int rightdepth = 0 ; TreeNode tmp = root; while (tmp.right != null ) { rightdepth++; tmp = tmp.right; } tmp = root; while (tmp.left != null ) { leftdepth++; tmp = tmp.left; } if (leftdepth == rightdepth) { return (2 <<rightdepth)-1 ; } return countNodes(root.left)+countNodes(root.right)+1 ; } }
11、平衡二叉树 力扣题目链接
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是
平衡二叉树
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:true
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4] 输出:false
示例 3:
提示:
树中的节点数在范围 [0, 5000] 内
-104 <= Node.val <= 104
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return true ; } int left = subLength(root.left); int right = subLength(root.right); if (Math.abs(left-right) > 1 ) { return false ; } return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right); } public int subLength (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return 0 ; } return Math.max(subLength(root.left),subLength(root.right))+1 ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) { return getLength(root)==-1 ?false :true ; } public int getLength (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return 0 ; } int leftLength = getLength(root.left); if (leftLength == -1 ) { return -1 ; } int rightLength = getLength(root.right); if (rightLength == -1 ) { return -1 ; } if (Math.abs(rightLength-leftLength) >1 ) { return -1 ; } return Math.max(rightLength,leftLength)+1 ; } }
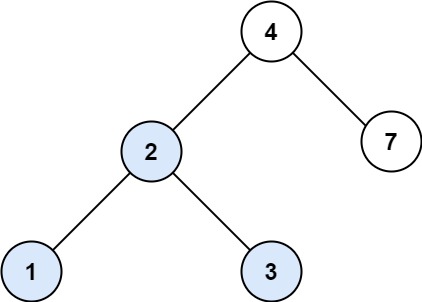
12、二叉树的所有路径 力扣题目链接
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
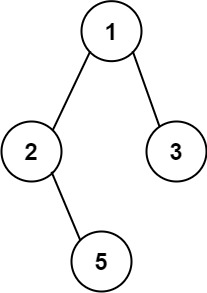
1 2 输入:root = [1,2,3,null,5] 输出:["1->2->5","1->3"]
示例 2:
提示:
树中节点的数目在范围 [1, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) { List<String> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) { return res; } List<Integer> paths = new ArrayList <>(); Backtrace (root,res,paths); return res; } public void Backtrace (TreeNode root,List<String> res,List<Integer> paths) { paths.add(root.val); if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i<paths.size()-1 ; i++) { sb.append(paths.get(i)).append("->" ); } sb.append(paths.get(paths.size()-1 )); res.add(sb.toString()); return ; } if (root.left != null ) { Backtrace(root.left,res,paths); paths.remove(paths.size()-1 ); } if (root.right != null ) { Backtrace(root.right,res,paths); paths.remove(paths.size()-1 ); } } }
一直往下遍历, 递归的终止条件时遇到左孩子和右孩子都为空,此时将路径转换为字符串并添加到结果列表,然后回溯到上一个节点继续遍历其他子节点。
13、左叶子之和 力扣题目链接
给定二叉树的根节点 root ,返回所有左叶子之和。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出: 24 解释: 在这个二叉树中,有两个左叶子,分别是 9 和 15,所以返回 24
示例 2:
提示:
节点数在 [1, 1000] 范围内
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) { int sum = 0 ; if (root == null ) return 0 ; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); while (size -- > 0 ) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left != null ) { queue.offer(node.left); if (node.left.left == null && node.left.right == null ){ sum += node.left.val; } } if (node.right != null ) queue.offer(node.right); } } return sum; } }
使用层次遍历法,由于不能直接判断本节点是不是左叶子节点,所以需要借助父亲节点进行判断。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; int leftVal = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left); int rightVal = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right); int midVal = 0 ; if (root.left != null && root.left.left==null && root.left.right==null ) { midVal += root.left.val; } int result = leftVal + midVal +rightVal; return result; } }
14、找树左下角的值 力扣题目链接
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: root = [2,1,3] 输出: 1
示例 2:
1 2 输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7] 输出: 7
提示:
二叉树的节点个数的范围是 [1,104]
-231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) { int result = 0 ; Queue <TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int length = queue.size(); if (length > 0 ) { TreeNode tmp = queue.peek(); result = tmp.val; } while (length > 0 ) { TreeNode tmp = queue.poll(); if (tmp.left != null ) { queue.offer(tmp.left); } if (tmp.right != null ) { queue.offer(tmp.right); } length--; } } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { private int Deep = -1 ; private int value = 0 ; public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) { value = root.val; findLeftValue(root,0 ); return value; } public void findLeftValue (TreeNode root,int deep) { if (root ==null ) return ; if (deep > Deep) { value = root.val; Deep = deep; } if (root.left !=null ) { findLeftValue(root.left,deep+1 ); } if (root.right !=null ) { findLeftValue(root.right,deep+1 ); } } }
通过确定访问的变量是不是处于最大深度的节点来确定。
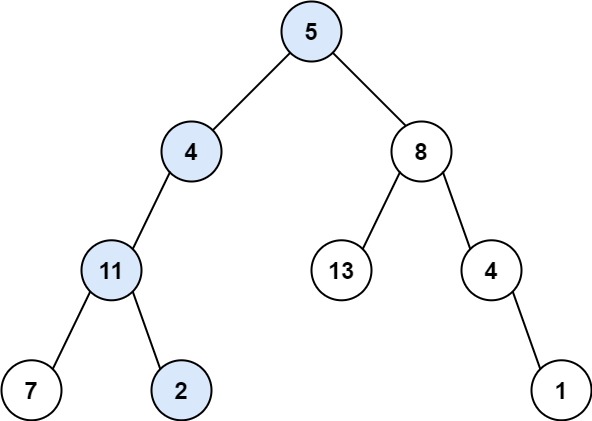
15、路径总和 力扣题目链接
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 输出:true 解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。
示例 2:
1 2 3 4 5 6 输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 输出:false 解释:树中存在两条根节点到叶子节点的路径: (1 --> 2): 和为 3 (1 --> 3): 和为 4 不存在 sum = 5 的根节点到叶子节点的路径。
示例 3:
1 2 3 输入:root = [], targetSum = 0 输出:false 解释:由于树是空的,所以不存在根节点到叶子节点的路径。
提示:
树中节点的数目在范围 [0, 5000] 内
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { if (root == null ) return false ; targetSum -= root.val; if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) { return targetSum == 0 ; } if (root.left != null ) { boolean leftResult = hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum); if (leftResult) { return true ; } } if (root.right != null ) { boolean rightResult = hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum); if (rightResult) { return true ; } } return false ; } }
用目标结果减去节点的值判断是否为0 来确定是否存在具体的路径。
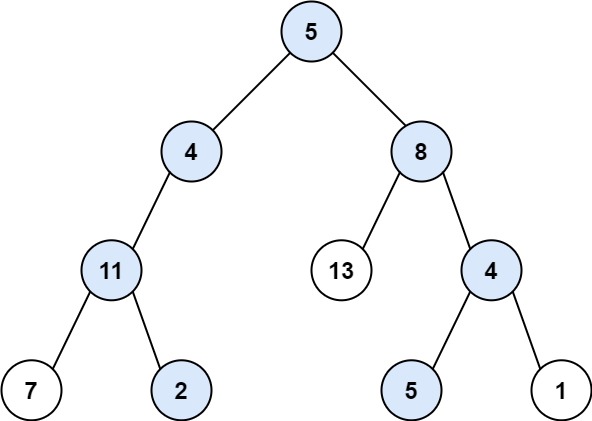
路径综合II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 输出:[]
示例 3:
1 2 输入:root = [1,2], targetSum = 0 输出:[]
提示:
树中节点总数在范围 [0, 5000] 内
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList <>(); pathFind(root,targetSum,tmp,result); return result; } public void pathFind (TreeNode root, int targetSum,List<Integer> tmp,List<List<Integer>> result) { if (root == null ) return ; tmp.add(root.val); targetSum -= root.val; if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) { if (targetSum == 0 ) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(tmp)); } return ; } if (root.left != null ) { pathFind(root.left,targetSum,tmp,result); tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1 ); } if (root.right != null ) { pathFind(root.right,targetSum,tmp,result); tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1 ); } } }
关键在于需要创建一个快照,因为直接使用引用的话,后续对tmp的修改会影响result中的数据。
16、从中序与后序遍历序列构建二叉树 力扣题目链接
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
1 2 输入:inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1] 输出:[-1]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { private Map<Integer,Integer>map; public TreeNode buildTree (int [] inorder, int [] postorder) { map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i=0 ; i<inorder.length; i++) { map.put(inorder[i],i); } TreeNode result = buildTree (inorder,0 ,inorder.length-1 ,postorder,0 ,postorder.length-1 ); return result; } public TreeNode buildTree (int [] inorder, int inbegin, int inend, int [] postorder, int postbegin, int postend) { if (inbegin > inend || postbegin > postend) { return null ; } int rootVal = postorder[postend]; int indexVal = map.get(rootVal); int leftSize = indexVal - inbegin; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (rootVal); root.left = buildTree (inorder,indexVal-leftSize,indexVal-1 ,postorder,postbegin,postbegin+leftSize-1 ); root.right = buildTree (inorder,indexVal+1 ,inend,postorder,postbegin+leftSize,postend-1 ); return root; } }
https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/description/
给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历 , inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历 ,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] 输出: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
1 2 输入: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1] 输出: [-1]
提示:
1 <= preorder.length <= 3000inorder.length == preorder.length-3000 <= preorder[i], inorder[i] <= 3000preorder 和 inorder 均 无重复 元素inorder 均出现在 preorderpreorder 保证 为二叉树的前序遍历序列inorder 保证 为二叉树的中序遍历序列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { private Map <Integer,Integer> map; public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) { map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i=0 ;i<inorder.length;i++) { map.put(inorder[i],i); } TreeNode result = buildTreeSolution(preorder,0 ,preorder.length-1 ,inorder,0 ,inorder.length-1 ); return result; } public TreeNode buildTreeSolution (int [] preorder, int preBegin, int preEnd,int [] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd) { if (preBegin > preEnd || inBegin > inEnd) { return null ; } int rootVal = preorder[preBegin]; int indexVal = map.get(rootVal); int leftSize = indexVal - inBegin; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (rootVal); root.left = buildTreeSolution(preorder,preBegin+1 ,preBegin+leftSize,inorder,inBegin,inBegin+leftSize); root.right = buildTreeSolution(preorder,preBegin+leftSize+1 ,preEnd,inorder,inBegin+leftSize+1 ,inEnd); return root; } }
都是以前序或者后序的开头或最后的一个元素 作为中序遍历数组的分界点。
17、最大二叉树 给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:
创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。
递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。
递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。
返回 nums 构建的最大二叉树* 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 输入:nums = [3,2,1,6,0,5] 输出:[6,3,5,null,2,0,null,null,1] 解释:递归调用如下所示: - [3,2,1,6,0,5] 中的最大值是 6 ,左边部分是 [3,2,1] ,右边部分是 [0,5] 。 - [3,2,1] 中的最大值是 3 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [2,1] 。 - 空数组,无子节点。 - [2,1] 中的最大值是 2 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [1] 。 - 空数组,无子节点。 - 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 1 的节点。 - [0,5] 中的最大值是 5 ,左边部分是 [0] ,右边部分是 [] 。 - 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 0 的节点。 - 空数组,无子节点。
示例 2:
1 2 输入:nums = [3,2,1] 输出:[3,null,2,null,1]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10000 <= nums[i] <= 1000nums 中的所有整数 互不相同
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 0 ) { return null ; } TreeNode result = construct(nums,0 ,nums.length-1 ); return result; } public TreeNode construct (int [] nums,int start, int end) { if (start > end) { return null ; } int max = nums[start]; int index = start ; for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { if (nums[i] > max) { max = nums[i]; index = i; } } TreeNode root = new TreeNode (max); root.left = construct(nums,start,index-1 ); root.right = construct(nums,index+1 ,end); return root; } }
18、合并二叉树 给你两棵二叉树: root1 和 root2 。
想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新二叉树。合并的规则是:如果两个节点重叠,那么将这两个节点的值相加作为合并后节点的新值;否则,不为 null 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
返回合并后的二叉树。
注意: 合并过程必须从两个树的根节点开始。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root1 = [1,3,2,5], root2 = [2,1,3,null,4,null,7] 输出:[3,4,5,5,4,null,7]
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root1 = [1], root2 = [1,2] 输出:[2,2]
提示:
两棵树中的节点数目在范围 [0, 2000] 内
-104 <= Node.val <= 104
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null ) { return root2; } if (root2 == null ) { return root1; } root1.val += root2.val; root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left); root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right); return root1; }
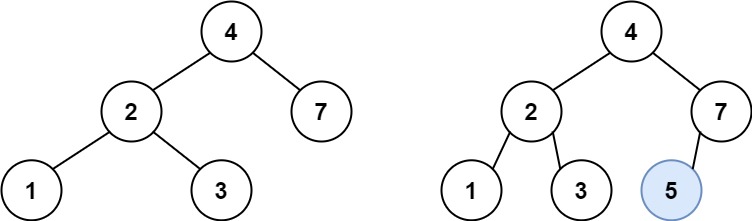
19、二叉搜索树中的搜索 给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和一个整数值 val。
你需要在 BST 中找到节点值等于 val 的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 null 。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 2 输出:[2,1,3]
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5 输出:[]
提示:
树中节点数在 [1, 5000] 范围内
1 <= Node.val <= 107root 是二叉搜索树1 <= val <= 107
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) { if (root == null || root.val == val) { return root; } TreeNode left = searchBST(root.left, val); if (left != null ) { return left; } return searchBST(root.right, val); } }
20、验证二叉搜索树 力扣题目链接
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
节点的左
子树
只包含
小于
当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [2,1,3] 输出:true
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6] 输出:false 解释:根节点的值是 5 ,但是右子节点的值是 4 。
提示:
树中节点数目范围在[1, 104] 内
-231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { private long prev = Long.MIN_VALUE; public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return true ; } boolean left = isValidBST(root.left); if (!left) { return false ; } if (prev >= root.val) { return false ; } prev = root.val; boolean right = isValidBST(root.right); return right; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) { List <Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); travel(root,list); for (int i = 1 ; i < list.size(); i++) { if (list.get(i) <= list.get(i-1 )) { return false ; } } return true ; } public void travel (TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) { if (root == null ) { return ; } travel(root.left,list); list.add(root.val); travel(root.right,list); } }
21、二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 力扣题目链接
给你一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,返回 树中任意两不同节点值之间的最小差值 。
差值是一个正数,其数值等于两值之差的绝对值。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [4,2,6,1,3] 输出:1
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [1,0,48,null,null,12,49] 输出:1
提示:
树中节点的数目范围是 [2, 104]
0 <= Node.val <= 105
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { private Integer prev = null ; private int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public int getMinimumDifference (TreeNode root) { travel(root); return min; } public void travel (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return ; } travel(root.left); if (prev != null ) { min = Math.min(min, root.val - prev); } prev = root.val; travel(root.right); } }
22、二叉搜索树中的众数 力扣题目链接
给你一个含重复值的二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root ,找出并返回 BST 中的所有 众数 (即,出现频率最高的元素)。
如果树中有不止一个众数,可以按 任意顺序 返回。
假定 BST 满足如下定义:
结点左子树中所含节点的值 小于等于 当前节点的值
结点右子树中所含节点的值 大于等于 当前节点的值
左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [1,null,2,2] 输出:[2]
示例 2:
提示:
树中节点的数目在范围 [1, 104] 内
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { private Integer prev = null ; private int count = 0 ; private int maxCount = 0 ; private List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); public int [] findMode(TreeNode root) { travel(root); return result.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray(); } public void travel (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return ; } travel(root.left); if (prev == null || root.val != prev) { count = 1 ; } else { count++; } if (count == maxCount) { result.add(root.val); } if (count > maxCount ) { maxCount = count; result.clear(); result.add(root.val); } prev = root.val; travel(root.right); }
23、二叉树的最近公共祖先 给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科 中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先 )。”
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 输出:3 解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 输出:5 解释:节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5 。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
示例 3:
1 2 输入:root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2 输出:1
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [2, 105] 内。
-109 <= Node.val <= 109所有 Node.val 互不相同 。
p != qp 和 q 均存在于给定的二叉树中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root == null || root == p || root == q) { return root; } TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); if (left != null && right != null ) { return root; } if (left != null ) { return left; } else { return right; } } }
假设我们在一个节点 root 开始搜索 p 和 q:
**当前节点是否为 null**:如果当前节点是 null,那显然这个子树中没有 p 和 q,我们返回 null。
**当前节点是否是 p 或 q**:如果当前节点正好是 p 或 q,那么这个节点直接可能是公共祖先,我们返回这个节点。
递归查找左右子树 :如果当前节点不是 p 或 q,我们继续在它的左子树和右子树中递归查找 p 和 q。
如果在左子树中找到一个非空结果,说明 p 或 q 在左子树中。
如果在右子树中找到一个非空结果,说明 p 或 q 在右子树中。
如果左右子树都返回非空的结果,说明 p 和 q 分别位于左右子树中,因此当前节点 root 就是它们的最近公共祖先。
如果只有一边返回了非空结果(例如左边有,右边没有),那说明 p 和 q 都位于左子树中,返回左边的结果。
返回值 :递归的结果就是我们所要的最近公共祖先。
23、二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科 中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先 )。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8 输出: 6 解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4 输出: 2 解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
所有节点的值都是唯一的。
p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { while (root != null ) { if (p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) { root = root.left; } else if (p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val) { root = root.right; } else { return root; } } return null ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root == null ) { return null ; } if (p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) { TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor (root.left,p,q); if (left != null ) { return left; } } if (p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val) { TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right ,p ,q); if (right != null ) { return right; } } return root; } }
24、二叉搜索树中的插入操作 给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和要插入树中的值 value ,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据 保证 ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。
注意 ,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回 任意有效的结果 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5 输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5] 解释:另一个满足题目要求可以通过的树是:
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [40,20,60,10,30,50,70], val = 25 输出:[40,20,60,10,30,50,70,null,null,25]
示例 3:
1 2 输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,null], val = 5 输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5]
提示:
树中的节点数将在 [0, 104]的范围内。
-108 <= Node.val <= 108所有值 Node.val 是 独一无二 的。
-108 <= val <= 108保证 val 在原始BST中不存在。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public TreeNode insertIntoBST (TreeNode root, int val) { if (root == null ) { return new TreeNode (val); } if (root.val > val) { root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left,val); } if (root.val < val) { root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right,val); } return root; } }
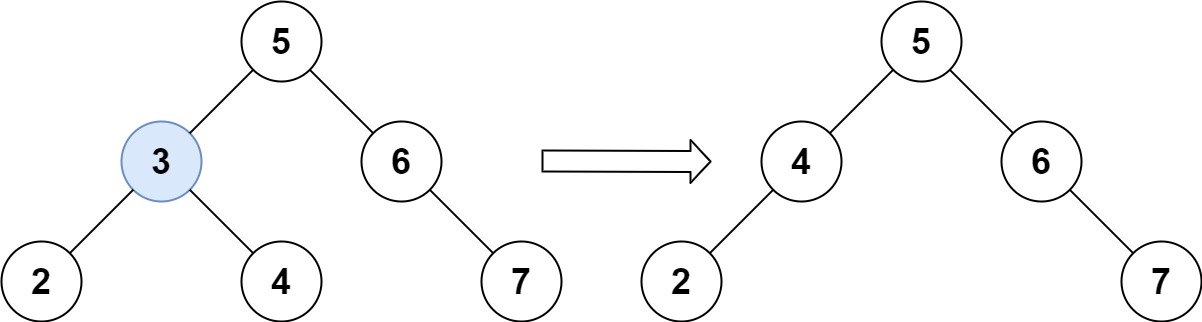
25、删除二叉搜索树中的节点 给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key ,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
首先找到需要删除的节点;
如果找到了,删除它。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 输入:root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 3 输出:[5,4,6,2,null,null,7] 解释:给定需要删除的节点值是 3,所以我们首先找到 3 这个节点,然后删除它。 一个正确的答案是 [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], 如下图所示。 另一个正确答案是 [5,2,6,null,4,null,7]。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 0 输出: [5,3,6,2,4,null,7] 解释: 二叉树不包含值为 0 的节点
示例 3:
1 2 输入: root = [], key = 0 输出: []
提示:
节点数的范围 [0, 104].
-105 <= Node.val <= 105节点值唯一
root 是合法的二叉搜索树-105 <= key <= 105
进阶: 要求算法时间复杂度为 O(h),h 为树的高度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public TreeNode deleteNode (TreeNode root, int key) { if (root == null ) { return root; } if (root.val == key) { if (root.left == null ) { return root.right; } if (root.right == null ) { return root.left; } TreeNode cur = root.right; while (cur.left != null ) { cur = cur.left; } cur.left = root.left; return root.right; } if (root.val < key) { root.right = deleteNode (root.right,key); } if (root.val > key) { root.left = deleteNode (root.left,key); } return root; } }
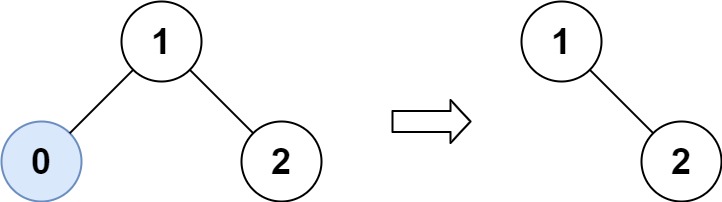
26、修剪二叉搜索树 给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,同时给定最小边界low 和最大边界 high。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[low, high]中。修剪树 不应该 改变保留在树中的元素的相对结构 (即,如果没有被移除,原有的父代子代关系都应当保留)。 可以证明,存在 唯一的答案 。
所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。注意,根节点可能会根据给定的边界发生改变。
示例 1:
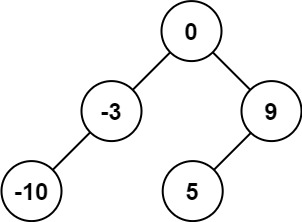
1 2 输入:root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2 输出:[1,null,2]
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3 输出:[3,2,null,1]
提示:
树中节点数在范围 [1, 104] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 104树中每个节点的值都是 唯一 的
题目数据保证输入是一棵有效的二叉搜索树
0 <= low <= high <= 104
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public TreeNode trimBST (TreeNode root, int low, int high) { if (root == null ) { return root; } if (root.val < low) { return trimBST(root.right,low,high); }else if (root.val > high) { return trimBST(root.left,low,high); }else { root.left = trimBST(root.left,low,high); root.right = trimBST(root.right,low,high); return root; } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int val) { this .val = val; } } public class TrimBST { public TreeNode trimBST (TreeNode root, int low, int high) { while (root != null && (root.val < low || root.val > high)) { if (root.val < low) { root = root.right; } else if (root.val > high) { root = root.left; } } TreeNode current = root; while (current != null ) { while (current.left != null && current.left.val < low) { current.left = current.left.right; } current = current.left; } current = root; while (current != null ) { while (current.right != null && current.right.val > high) { current.right = current.right.left; } current = current.right; } return root; } public static void main (String[] args) { TreeNode root = new TreeNode (3 ); root.left = new TreeNode (0 ); root.right = new TreeNode (4 ); root.left.right = new TreeNode (2 ); root.left.right.left = new TreeNode (1 ); int low = 1 , high = 3 ; TrimBST trimmer = new TrimBST (); TreeNode trimmedRoot = trimmer.trimBST(root, low, high); printTree(trimmedRoot); } private static void printTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return ; java.util.Queue<TreeNode> queue = new java .util.LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); System.out.print(node.val + " " ); if (node.left != null ) queue.offer(node.left); if (node.right != null ) queue.offer(node.right); } System.out.println(); } }
27、将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请你将其转换为一棵
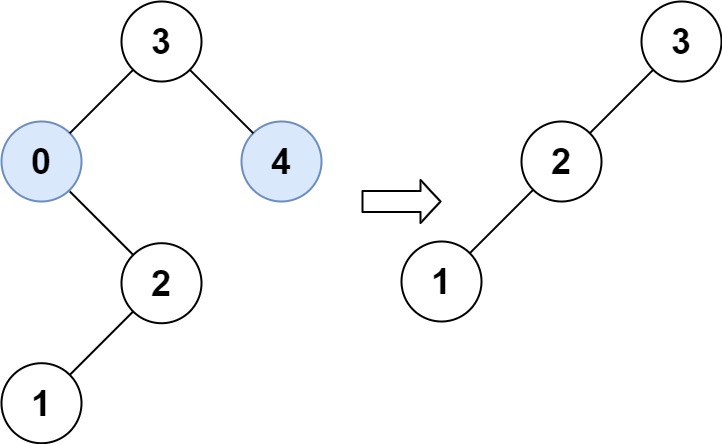
平衡
二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9] 输出:[0,-3,9,-10,null,5] 解释:[0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] 也将被视为正确答案:
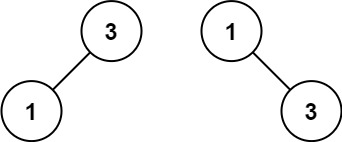
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:nums = [1,3] 输出:[3,1] 解释:[1,null,3] 和 [3,1] 都是高度平衡二叉搜索树。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-104 <= nums[i] <= 104nums 按 严格递增 顺序排列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST (int [] nums) { return sortedArrayToBST(nums, 0 , nums.length-1 ); } public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST (int [] nums, int start, int end) { if (start > end) { return null ; } int mid = start + (end - start)/2 ; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (nums[mid]); root.left = sortedArrayToBST(nums,start,mid-1 ); root.right = sortedArrayToBST(nums,mid+1 ,end); return root; } }
28、把二叉搜索树转换为累加树 给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。
节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。
左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
注意: 本题和 1038: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/ 相同
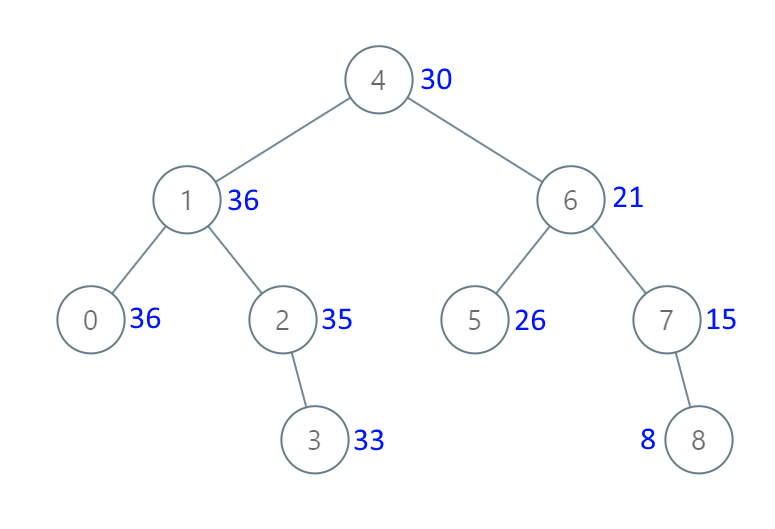
示例 1:
1 2 输入:[4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8] 输出:[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [0,null,1] 输出:[1,null,1]
示例 3:
1 2 输入:root = [1,0,2] 输出:[3,3,2]
示例 4:
1 2 输入:root = [3,2,4,1] 输出:[7,9,4,10]
提示:
树中的节点数介于 0 和 104 之间。
每个节点的值介于 -104 和 104 之间。
树中的所有值 互不相同 。
给定的树为二叉搜索树。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { private int sum = 0 ; public TreeNode convertBST (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return root; } convertBST(root.right); sum += root.val; root.val = sum; convertBST(root.left); return root; } }